How to defend against Account Takeovers
Learn about account takeover threats, protection strategies, and detection methods to secure your digital accounts and prevent unauthorised access.
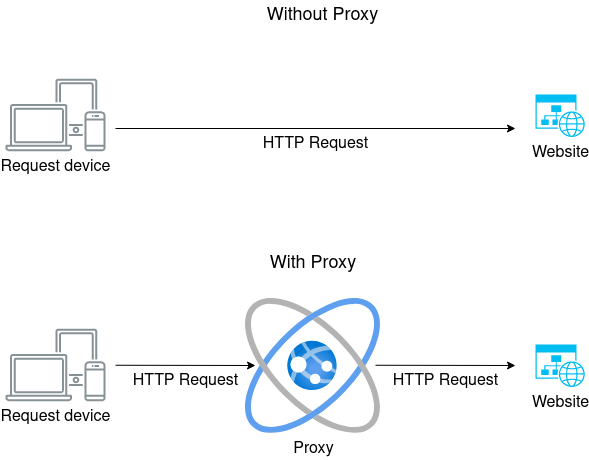
A residential proxy is a type of proxy server that uses an IP address provided by an Internet Service Provider (ISP), not a data center. Each residential proxy address appears as a regular user to websites, offering anonymity and avoiding detection as a proxy by most site security systems.
Residential proxies route your internet traffic through an intermediary server. This server changes your IP address before sending your request to the target website. As a result, the website sees the request as coming from the proxy's IP address instead of your actual IP address.
Here's a practical example: When you're in New York and want to check how a website appears to users in London, you could route your connection through a residential proxy in the UK. To the website, your traffic would appear to come from a real home in London, complete with a legitimate UK Internet Service Provider and appropriate geographic data.
At first glance, a residential proxy solves the same problem as VPNs, however they offer significant advantages over a VPN.
When you use a residential proxy, you're borrowing the identity of a real ISP customer, complete with their ISP's infrastructure characteristics. This includes helpful features like:
Carrier-Grade NAT (CGNAT): Many residential IPs operate behind CGNAT, which is a standard practice for ISPs. This means multiple users share the same public IP - exactly what you'd expect to see from a residential connection. When websites see traffic coming through CGNAT, it strongly signals legitimate residential origin. It also makes blocking at the IP level undesirable, as many legitimate users would also be blocked.
Mobile Network Characteristics: Residential proxies that utilize mobile networks exhibit natural IP rotation and movement patterns. As mobile devices switch between cell towers or from mobile data to WiFi, their IPs change naturally. This creates organic-looking patterns that are hard to distinguish from regular user behavior.
In contrast, VPNs typically have several limitations that make them easier to detect:
Residential Proxies are increasingly used by fraudsters and scammers as they provide:
Residential proxy networks are formed through various distribution channels, with some being more ethical than others. The key methods include:
SDK Integration: Many mobile apps incorporate SDKs that enable bandwidth sharing. When users install these apps, they often include terms of service that permit bandwidth sharing, though this may be buried in legal text.
Free VPN Services: Some VPN providers offer free services that, in their terms of service, specify that users' bandwidth may be shared. While connected, these VPNs may route other users' traffic through the connection.
Browser Extensions: Like SDK integration and free VPN apps, browser extensions might enable sharing of an internet connection with third parties.
Compromised Devices/routers: Some networks are formed by malicious or state actors by hacking routers or devices, Camaro Dragon was responsible for one such network via TP-Link routers.
Mobile Farms: Special hardware where 10s or 100s of Mobile Sim cards to be installed can create dedicated residential/mobile proxy networks where the physical hardware can be relocated to connect to different mobile towers.
These IPs are made available by sometimes unwitting users installing applications, like free VPNs, on their phone or computer, that effectively makes the device's internet connection available to the proxy network provider. The provider can then route internet requests through that device for their customers.
Yes, as long as the proxy was formed legally, with the full knowledge and consent of the device owner.
As the proxy is usually hosted on a user's device, it is not necessarily using a fixed IP address. The device might change IP address several times a day. Those IP addresses will also have non proxy users mixed in making requests.
For example, in the case of a proxy on a mobile phone, the IP address will be from the mobile tower the device connects to. 1000s of individual devices might be using the same IP address.
Their mobility and dynamic nature mean simply blocking the IP address is ineffective and will inevitably block real users too. By the time the IP address has been blocked, the proxy has probably moved on.
Traditional methods of IP Intelligence are ineffective against residential proxies.
Static analysis of an IP's reputation no longer works. Proxy usage has to be evaluated on a per-request basis via deep inspection of the connecting request. Peakhour's residential proxy detection service is one such service capable of detecting residential proxies.
Learn about account takeover threats, protection strategies, and detection methods to secure your digital accounts and prevent unauthorised access.
An overview of Account Takeover Attacks
A step-by-step breakdown of how credential stuffing attacks are carried out, from obtaining stolen credentials to bypassing defenses and taking over accounts.
An introduction to Anycast DNS
A quick description about what an Apex Domain is.
Learn the essential best practices for managing and rotating API keys to enhance security, prevent unauthorized access, and minimize the impact of key compromise.
© PEAKHOUR.IO PTY LTD 2025 ABN 76 619 930 826 All rights reserved.